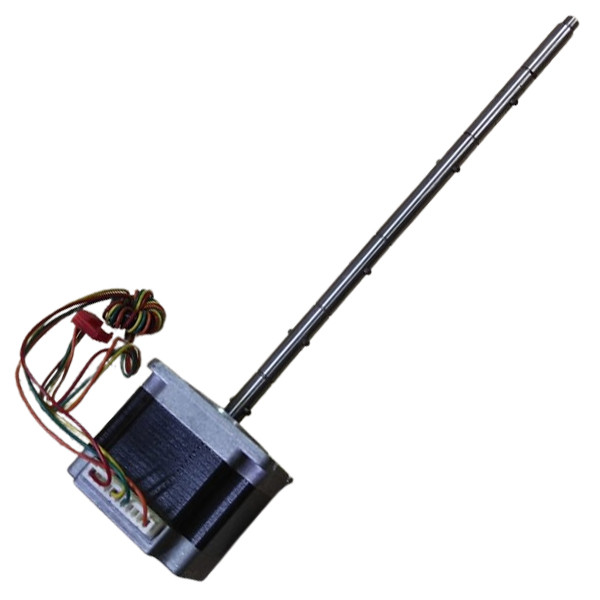
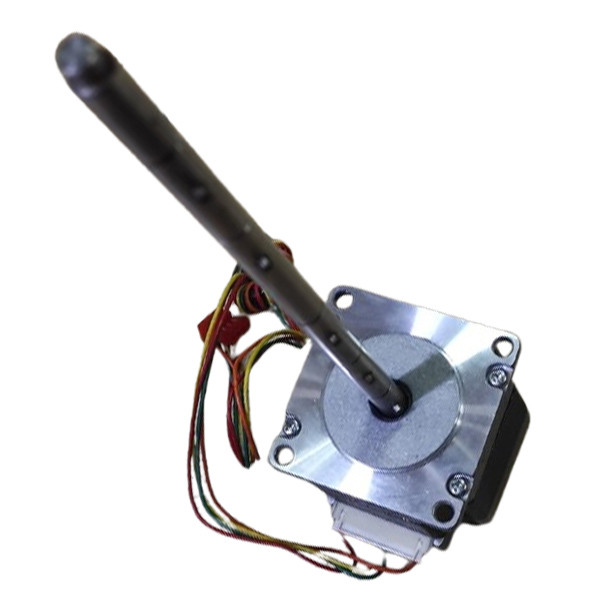
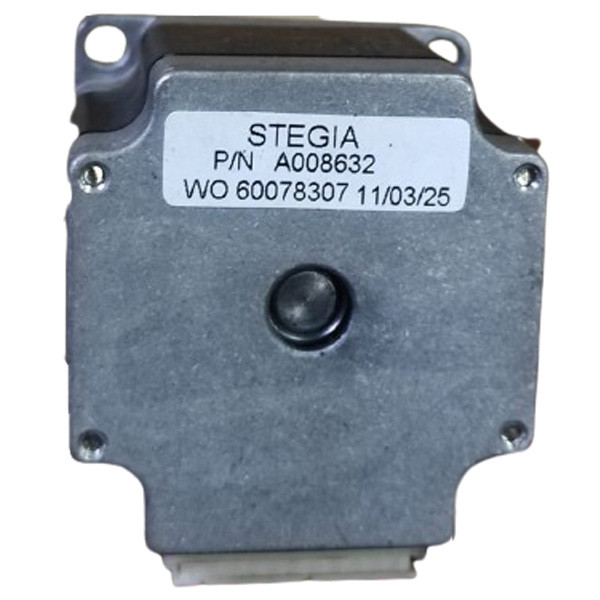
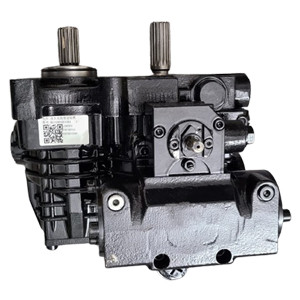
Stegia Stepper Motor A008632 | Brand New |
(0 reviews)
Sold by:
Inhouse product
Inhouse product
Price:
৳3,500.00
/1
Share:
Top Selling Products
-
REXROTH Hydraulic Valve R901226876 | New |
৳10,500.00
Stegia Stepper Motor A008632 | Original |
Motor
Part No: A008632
Brand: Stegia
Condition: New
Availability: In Stock
Ships: Fast and Reliable Shipping
Brand New
There have been no reviews for this product yet.
Related products
৳13,500.00
Minebea 23LM-C057-03 Bipolar Stepper Motor
৳145,000.00
Hydraulic Gear Motor RGV4G04010001 | Brand New |
Premium Quality Best Electric Motor Price in Bangladesh
৳260,000.00